In a world increasingly driven by artificial intelligence (AI), ensuring that these systems are developed, deployed, and managed responsibly is no longer a choice—it’s a necessity. Enter ISO/IEC 42001, the first international standard dedicated to Artificial Intelligence Management Systems (AIMS). This standard offers a structured framework for organizations to govern their AI initiatives effectively, ensuring ethical, secure, and transparent AI practices.
Understanding ISO/IEC 42001
ISO/IEC 42001 establishes a foundation for managing AI systems across their entire lifecycle. From conception and development to deployment and monitoring, this standard emphasizes accountability and continuous improvement.
But why is such a standard crucial? The answer lies in the dual nature of AI: its potential for transformative benefits and its risks, including biases, security vulnerabilities, and unintended consequences. ISO/IEC 42001 helps organizations navigate these complexities.
ISO/IEC 42001 is a voluntary standard, meaning that anyone can decide to adopt it if it benefits their organization. Organizations operating in the technological industry are however encouraged more than others.
Key Features of ISO/IEC 42001
-
AI Management System (AIMS):
At its core, ISO/IEC 42001 introduces the concept of an AI Management System. AIMS integrates AI governance into an organization’s existing management framework, ensuring that AI practices align with business objectives, regulatory requirements, and ethical standards:- Ensures a systematic approach to AI governance.
- Promotes continuous improvement and risk management.
- Facilitates integration with other standards like ISO 27001 (Information Security) and ISO 9001 (Quality Management).
-
Risk and Impact Assessments:
One of the defining elements of ISO/IEC 42001 is its emphasis on comprehensive risk and impact assessments.- AI Risk Assessment: Identifies potential risks throughout the AI lifecycle, from data collection to algorithm performance and system deployment.
- AI Impact Assessment: Evaluates the societal, ethical, and organizational consequences of AI systems.
-
Data Protection and Security:
Given the data-intensive nature of AI, ISO/IEC 42001 mandates robust data protection measures.- Ensures compliance with global privacy laws, such as GDPR.
- Safeguards AI systems against cyber threats.
- Promotes secure data handling and storage practices.
Why Adopt ISO/IEC 42001?
Adopting ISO/IEC 42001 offers organizations several strategic advantages, especially as AI regulations continue to evolve globally.
1. Enhanced Trust and Reputation:
Certification demonstrates an organization’s commitment to responsible AI, which can significantly enhance trust among stakeholders, including customers, partners, and regulators.
2. Regulatory Preparedness:
With AI regulations becoming stricter, ISO/IEC 42001 helps organizations stay ahead of legal requirements, minimizing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
3. Operational Efficiency:
By providing a structured approach to AI management, the standard streamlines processes, reduces inefficiencies, and mitigates risks, ultimately leading to cost savings.
Implementing ISO/IEC 42001: A Step-by-Step Guide
Successfully implementing ISO/IEC 42001 involves a strategic approach. Below is a high-level roadmap to help organizations get started:
1. Understand the Standard
The first step in implementing ISO/IEC 42001 is to fully understand the standard’s scope, requirements, and objectives. This involves more than a simple overview—it requires a deep dive into the framework to comprehend how it applies to your organization.
Start by studying the official documentation, focusing on key areas such as governance, risk management, and operational controls. Familiarizing yourself with the standard’s principles—like transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement—will help you align your AI practices with its requirements. Additionally, consider participating in relevant training sessions or consulting with experts to clarify complex aspects and gain practical insights.
This foundational understanding is crucial for building a compliant and effective AI management system tailored to your organization’s needs.
2. Engage Stakeholders
AI governance is not solely the responsibility of IT teams; it requires collaboration across various departments. Each function brings critical expertise to the table. Legal teams ensure compliance with regulations and ethical standards, compliance officers align practices with industry norms, and executive leadership provides strategic direction and oversight. Effective AI governance depends on this collective effort to address the complex challenges posed by AI systems.
-
Communicate the importance of ISO/IEC 42001 to stakeholders:
Highlight how the standard supports the organization’s broader goals, such as mitigating risks, enhancing trust, and ensuring regulatory compliance. Tailor the message to each department, emphasizing their specific contributions to implementing and maintaining the AI Management System (AIMS). -
Engage top management to drive organizational support:
Leadership plays a crucial role in setting the tone and ensuring alignment across the organization. Their involvement ensures that AI governance is prioritized and adequately resourced, reinforcing its importance as a strategic initiative.
3. Conduct a Gap Analysis
To effectively implement ISO/IEC 42001, organizations must first evaluate their current AI practices and processes against the standard’s requirements. This step is critical for understanding how well your existing systems align with the framework and identifying areas that need attention. Here’s how to approach it:
-
Review existing policies, procedures, and controls:
Examine the frameworks currently in place for managing AI systems. Focus on key areas such as risk management, ethical considerations, and data security. -
Assess alignment with ISO/IEC 42001 requirements:
Compare your current practices to the standard’s components to identify strengths and weaknesses. -
Identify gaps in current practices:
Look for areas where your organization falls short, such as insufficient risk assessments, lack of formal governance structures, or inadequate monitoring processes. -
Consider organizational factors:
Evaluate the culture, resource availability, and staff competencies related to AI governance, as these can impact your ability to meet the standard’s requirements.
4. Develop an Implementation Plan
Once the gap analysis is complete, the next step is to create a detailed roadmap for implementing ISO/IEC 42001. This roadmap serves as a strategic guide, outlining the steps your organization needs to take to close identified gaps and achieve compliance. It should provide a clear and structured plan to ensure a smooth implementation process. Key elements to include are timelines, assigned responsibilities, and resource allocation.
-
Establish clear timelines and milestones:
Define specific deadlines for each phase of the implementation, from policy development and process redesign to training and audits. Setting realistic milestones helps track progress and ensures accountability. -
Assign roles and responsibilities:
Identify the individuals or teams responsible for each task. This includes not only technical teams but also legal, compliance, and operational staff who will play a role in governance and oversight. -
Allocate necessary resources:
Determine the financial, human, and technological resources required for implementation. This may involve investing in new tools, hiring additional personnel, or providing training for existing staff. -
Incorporate risk mitigation strategies:
Include contingency plans for potential challenges, such as delays or resource constraints, to keep the implementation on track. -
Establish a communication plan:
Ensure regular updates are provided to all stakeholders to maintain alignment and momentum throughout the implementation process.
5. Implement AIMS
Integrating the AI Management System (AIMS) into your existing organizational processes is a crucial step in implementing ISO/IEC 42001. This involves embedding AI governance into the daily operations of your organization to ensure that AI-related activities are managed consistently and effectively. The integration process requires the establishment of new policies, procedures, and controls tailored to managing AI risks.
-
Develop and formalize new policies and procedures:
Create clear, comprehensive policies that address key aspects of AI governance, such as ethical use, data privacy, and algorithm accountability. These policies should be aligned with your organization’s strategic objectives and regulatory requirements. -
Implement robust controls for AI risk management:
Establish specific controls to mitigate risks associated with AI systems. This includes processes for data validation, bias detection, and algorithm performance monitoring. -
Align AIMS with existing management systems:
Ensure that AIMS works seamlessly with other frameworks, such as those for information security (ISO 27001) or quality management (ISO 9001). This alignment avoids duplication of effort and creates a unified governance structure. -
Embed AI governance into operational workflows:
Integrate AIMS-related tasks, such as regular risk assessments and performance reviews, into the day-to-day workflows of relevant departments. -
Provide training and awareness programs:
Educate employees on the new policies and controls to ensure they understand their roles and responsibilities in managing AI systems effectively.
6. Monitor and Improve
ISO/IEC 42001 places a strong emphasis on continuous improvement to ensure that your AI Management System (AIMS) remains effective and relevant over time. AI technologies, risks, and regulatory landscapes are constantly evolving, so organizations must regularly assess and refine their governance practices to stay ahead.
-
Conduct regular reviews and audits:
Schedule periodic evaluations of your AIMS to identify areas for improvement. This includes both internal audits and external assessments to ensure ongoing compliance with the standard. -
Adapt to emerging risks and technologies:
As new risks and AI technologies arise, update your risk management strategies and controls accordingly. Staying proactive helps prevent issues before they escalate. -
Monitor changes in regulatory requirements:
Keep track of developments in AI-related regulations and adjust your AIMS to ensure continued compliance. This is especially important in industries with rapidly changing legal frameworks. -
Incorporate feedback and lessons learned:
Use insights from incidents, stakeholder feedback, and performance metrics to refine your processes and enhance your AI governance practices. -
Foster a culture of continuous improvement:
Encourage all employees to contribute to the evolution of your AIMS by sharing ideas and identifying potential improvements in their day-to-day work.
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Implementing ISO/IEC 42001 is not without its challenges. However, with the right approach, organizations can overcome these obstacles effectively.
1. Integration with Existing Systems:
Integrating the AI Management System (AIMS) with your existing management systems, such as those for information security or quality management, can be a complex task. Organizations often face challenges in aligning new AI governance processes with established workflows and frameworks. However, a well-planned, phased implementation approach can help mitigate these difficulties and ensure a smooth transition.
-
Break the implementation into manageable phases:
Start with foundational elements, such as policy development and risk assessment, before moving on to more complex areas like system integration and performance monitoring. -
Leverage existing frameworks:
Identify synergies with current management systems (e.g., ISO 27001 or ISO 9001) to streamline processes and reduce duplication of effort. -
Pilot key components:
Test new AIMS elements in smaller, controlled environments to identify potential issues and refine processes before full-scale implementation. -
Provide incremental training and support:
Equip teams with the knowledge and tools they need at each phase to build confidence and competence in managing AI governance.
2. Addressing Complex AI Risks:
AI risks are inherently multifaceted, encompassing a wide range of challenges that organizations must proactively address. These risks can stem from various sources, including biases in data, unintended outcomes from algorithmic decisions, and vulnerabilities to cyber threats. Managing these complexities requires a comprehensive and well-structured approach.
-
Address data biases and fairness issues:
Implement rigorous data validation and preprocessing methods to minimize biases that could lead to discriminatory or unfair AI outcomes. -
Mitigate unintended algorithmic behaviors:
Regularly test and monitor AI systems to detect and correct any unexpected behaviors or inaccuracies in their decision-making processes. -
Strengthen cybersecurity measures:
Protect AI systems from potential cyberattacks by adopting advanced security protocols and conducting regular vulnerability assessments. -
Develop a culture of vigilance and accountability:
Foster an organizational mindset that prioritizes risk awareness and encourages all stakeholders to actively participate in identifying and mitigating AI-related risks.
3. Resource Constraints:
For smaller organizations, implementing ISO/IEC 42001 can be particularly challenging due to limited resources, such as budget, staff, or technical expertise. However, with a strategic approach, these challenges can be effectively managed to achieve compliance and build a robust AI governance framework.
-
Prioritize critical areas first:
Focus on high-impact areas of the AI Management System (AIMS), such as risk management, data protection, and compliance with key regulations. This ensures that limited resources are directed toward the most essential aspects of governance. -
Leverage external expertise:
Partner with consultants or third-party specialists who can provide guidance and support throughout the implementation process. External experts can offer valuable insights, help streamline efforts, and fill gaps in technical knowledge. -
Adopt scalable solutions:
Invest in tools and platforms that can grow with your organization, allowing you to start small and expand your AI governance capabilities over time. -
Utilize shared resources and training:
Access online resources, workshops, and training programs tailored to smaller organizations to build internal capacity without overextending your budget.
Certification Process
ISO/IEC 42001 certification involves an external audit conducted by an accredited certification body. The process typically includes the following steps:
-
Audit:
The certification body evaluates the organization's compliance with ISO/IEC 42001 requirements. -
Certification Issuance:
Upon successful completion of the audit, the organization receives certification, which is valid for three years. Annual surveillance audits ensure ongoing compliance.
The Future of ISO/IEC 42001
As AI continues to evolve, so too will the standards that govern its use. ISO/IEC 42001 is designed to adapt to these changes, ensuring that organizations can manage emerging risks and leverage new opportunities effectively.
Looking Ahead:
- We can expect updates to ISO/IEC 42001 as AI technologies and regulations evolve.
- Organizations that adopt this standard now will be better positioned to adapt to future changes and maintain a competitive edge.
Implement your AIMS with Brainframe
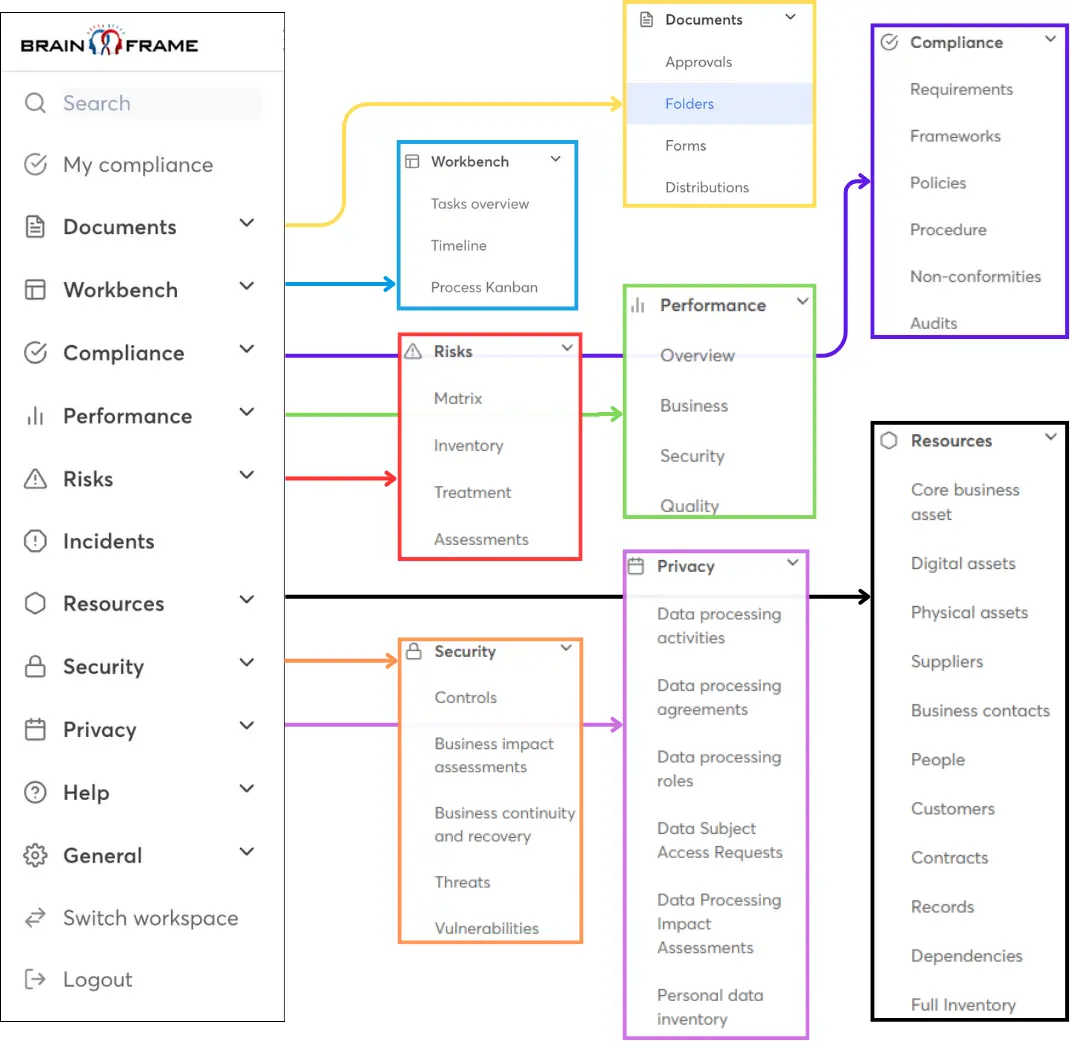
It is practically impossible to properly implement an AIMS as required by ISO/IEC 42001 without using a dedicated tool for it. Luckily, Brainframe can help. It provides a centralized tool where you can create, store, share, and track your policies and procedures related to your AIMS initiatives.
With the Risk module, you can stay on top of your risk assessments directly inside the tool, configure all your AI-related risks, visualize the risk evolutions of your AI assets and processes, and have a constantly available and up-to-date proof of compliance for your audits.
To easily identify dependencies between your operational and your AI processes, Brainframe provides a helicopter view where you can link any asset or process to another, to ensure you have a good visibility on the interdependencies between them.
It also gives you the option to assign roles and responsibilities, which will come in handy when you need to assign the responsibility of an AI process to a specific employee or board member. Through Brainframe, you can directly notify them about measures to be taken, reviews to be performed, or approvals to be given. You can then track their progress in the Task module, in a Kanban view.
Brainframe allows you to integrate your AIMS with your ISMS (e.g ISO 27001), identify the duplicates, and keep track of both of them inside the same tool.
PECB Resources
Check out our ISO/IEC 42001 related training courses and certifications to advance your career. The PECB certified ISO/IEC 42001 Lead Implementer and Lead Auditor certifications offer comprehensive training on implementing and auditing AI Management Systems. These certifications are designed to equip professionals with the skills and knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of AI governance, ensuring their organizations meet ISO/IEC 42001 requirements. By completing these courses, you’ll not only enhance your expertise but also position yourself as a key player in the rapidly evolving field of AI compliance and management.
Final Thoughts
In an era where AI is reshaping industries and societies, ISO/IEC 42001 provides a much-needed framework for responsible AI governance. By adopting this standard, organizations can not only mitigate risks but also unlock the full potential of AI in a secure, ethical, and sustainable manner.
Key Takeaways:
- ISO/IEC 42001 is the first international standard for AI Management Systems.
- It provides a structured framework for managing AI risks and ensuring compliance.
- Adoption of this standard enhances trust, operational efficiency, and regulatory preparedness.
- Implementation involves a systematic approach, from stakeholder engagement to continuous improvement.
For organizations looking to stay ahead in the AI game, ISO/IEC 42001 is not just an option—it’s a strategic imperative.